Σερραπεπτάση: το θαυματουργό ένζυμο
Το ένζυμο Σερραπεπτάση (Serrapeptase) χρησιμοποιείται ευρέως σε διάφορες ειδικότητες, όπως χειρουργική, ορθοπεδική, ωτορινολαρυγγολογία, γυναικολογία και οδοντιατρική για την ισχυρή αντιφλεγμονώδη δράση και την αποτελεσματικότητά του απέναντι στα οιδήματα.
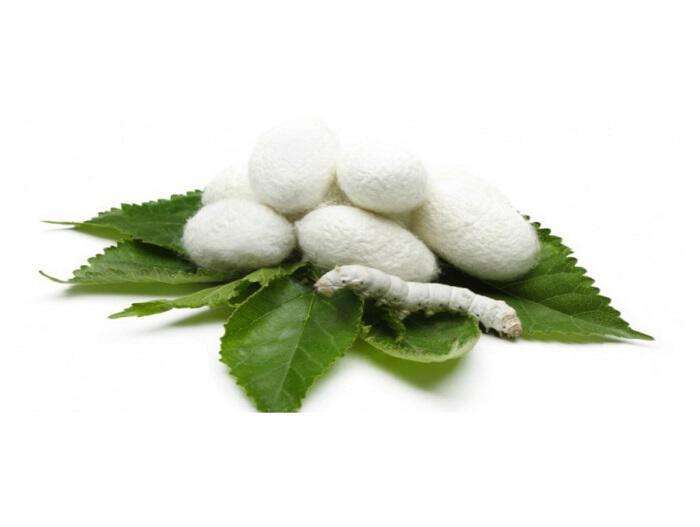
Το βακτήριο Serratia mercesans Ε1 παράγει την Serrapeptase , ένα ένζυμο που επιτρέπει στον μεταξοσκώληκα να διαλύσει το μεταξωτό του κουκούλι και να βγει μετά την μεταμόρφωσή του. Το ένζυμο αυτό βρέθηκε σε μεταξοσκώληκες και έχει την ικανότητα να επιζεί στον πεπτικό σωλήνα και να παραμένει ενεργό διαμέσου της κυκλοφορίας σε όλο το σώμα, γεγονός που μεγιστοποιεί τα θεραπευτικά της αποτελέσματα. Αυτό το πρωτεολυτικό ένζυμο, διασπά τις πρωτεΐνες σε μικρότερα συστατικά, τα αμινοξέα. Απομονώνεται από βακτήρια που εντοπίζονται στο σάλιο του μεταξοσκώληκα. Είναι αυτά τα ένζυμα, που βοηθούν τους μεταξοσκώληκες να σπάσουν το κουκούλι τους και να βγουν έξω.

Η βασική δράση του ενζύμου της Σερραπεπτάσης είναι η δυνατότητά του να τρώει, στην κυριοξεξία, τους μη ζωντανούς σχηματισμούς μέσα στο σώμα μας όπως τις φλεγμονές, τις λιπώδεις κύστεις, την βλέννα, τους θρόμβους, την αρτηριακή πλάκα, το λίπος στην κυκλοφορία του αίματος, τις υδατικές κύστες.
Καθώς ο άνθρωπος μεγαλώνει είναι επόμενο να συσσωρεύονται, ανάλογα φυσικά με το ιστορικό του καθενός, κάποιες αλλοιώσεις στους ιστούς, στο αίμα και στα οστά που σχηματίζουν το σώμα. Η ηλικία προκαλεί την εμφάνιση φλεγμονών, πόνου, αρτηριακών αποθέσεων και πιθανών άλλων ανεπιθύμητων συμπτωμάτων. Για αυτές ακριβώς τις περιπτώσεις η σερραπεπτάση μπορεί να αντιμετωπίσει έγκαιρα προβλήματα υγείας, καθώς το ένζυμο αυτό είναι δραστικό, απαιτεί μικρές δόσεις και είναι οικονομικά προσιτό.
Οι ανοσιολόγοι και οι ερευνητές στον τομέα της υγείας έχουν πιστοποιήσει ότι πολλές συχνές ασθένειες και παθήσεις της υγείας προκαλούνται από τις χρόνιες φλεγμονές. Αρκετοί γιατροί, με βάση αποτελέσματα μελετών και εμπειρίας από χρήση σε άλλους ασθενείς, συνιστούν την χορήγηση για διάστημα 3-5 μηνών σε κάθε ενήλικα ηλικίας άνω των 40 ετών. Το σκεπτικό πίσω απο αυτή τη σύσταση είναι ότι με την πάροδο των χρόνων το σώμα καταπονείται και σε διάφορα σημεία δημιουργούνται φλεγμονές, κύστες, ή θρομβώσεις οι οποίες μπορεί να μετατραπούν σε χρόνιες, ανεξάρτητα αν θα γίνουν άμεσα και έγκαιρα αντιληπτές. Οι πωλήσεις της Σερραπεπτάσης σε παγκόσμιο επίπεδο λέγεται ότι ξεπερνούν τα 5 δισ δολάρια ανά έτος και έχει κερδίσει τον τίτλο του “Θαυματουργού Ένζυμου” (the Miracle Enzyme).
H Serrapeptase χρησιμοποιείται για: •Πόνο κάθε είδους και κάθε είδους φλεγμονή. •Αρθρίτιδα, σκλήρυνση κατά πλάκας, ρευματοειδή αρθρίτιδα. •Λύκο. •Πονοκεφάλους και ημικρανίες, χρόνιες λοιμώξεις του αυτιού, ωτίτιδες. • Εμφύσημα, βρογχίτιδα, πνευμονική φυματίωση, βρογχικό άσθμα, βρογχιεκτασία, ινοκυστική ίνωση πνευμόνων. • Ιγμορίτιδα και καταρροή, χρόνια βλέννα στον ρινοφάρυγγα. •Αθλητικές κακώσεις, τραυματικό οίδημα, μετεγχειρητικό οίδημα, σύνδρομο καρπιαίου σωλήνα. •Φλεγμονώδεις νόσους των εντέρων (του Crohn, Κολίτιδα κλπ..) ινοκυστική μαστίτιδα, ενδομητρίωση,ινομυώματα… •Χρόνιες φλεγμονές στους μύες π.χ. Ινομυαλγία. •Καρδιαγγειακή υγεία, πρόληψη και θεραπεία θρομβωτικών σχηματισμών, αρτηριοσκλήρωση, λιπίδια αίματος, χοληστερίνη. •Φλεβίτιδα, θρομβοφλεβίτιδα. •Σημαντικό βοήθημα στα αυτοάνοσα νοσήματα, χωρίς να καταστέλλει το ανοσοποιητικό.
Με μία φράση η Serrapeptase συνιστάται για ένα πιο καθαρό καρδιαγγειακό σύστημα, καθαρότερο αναπνευστικό σύστημα και ένα σώμα με λιγότερους πόνους και φλεγμονές.
Παρενέργειες & προφυλάξεις στην χρήση της Serrapeptase
Η χρήση της Serrapeptase, με βάση τα στοιχεία των τελευταίων ετών φαίνεται να είναι ασφαλής, χωρίς παρενέργειες, όσον αφορά τους ενήλικες και με την προϋπόθεση ότι λαμβάνεται όπως προβλέπεται κατόπιν συνεννόησης με κάποιον ιατρό.
Πηγές:
Αναφορές – Βιβλιογραφία
- Bhagat S, Agarwal M, Roy V Serratiopeptidase: a systematic review of the existing evidence . Int J Surg. (2013)
- Badhe RV, et al Media optimization studies for Serratiopeptidase production from Serratia marcescens ATCC 13880 . Hindustan Antibiot Bull. (2009)
- Purification and characterization of four proteases from a clinical isolate of Serratia marcescens kums 3958
- Pansuriya R, Singhal R Effects of dissolved oxygen and agitation on production of serratiopeptidase by Serratia marcescens NRRL B-23112 in stirred tank bioreactor and its kinetic modeling . J Microbiol Biotechnol. (2011)
- CASTANEDA-AGULLO M Studies on the biosynthesis of extracellular proteases by bacteria. I. Serratia marcescens, synthetic and gelatin media . J Gen Physiol. (1956)
- Bromke BJ, Hammel JM Regulation of extracellular protease formation by Serratia marcescens . Can J Microbiol. (1979)
- Matsumoto K, et al Purification and characterization of four proteases from a clinical isolate of Serratia marcescens kums 3958 . J Bacteriol. (1984)
- Selan L, et al Proteolytic enzymes: a new treatment strategy for prosthetic infections . Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (1993)
- Cloning and sequencing of Serratia protease gene
- Easily absorbable enzyme preparation
- Umashankar MS, Sachdeva RK, Gulati M Aquasomes: a promising carrier for peptides and protein delivery . Nanomedicine. (2010)
- Rawat M, et al Development and in vitro evaluation of alginate gel-encapsulated, chitosan-coated ceramic nanocores for oral delivery of enzyme . Drug Dev Ind Pharm. (2008)
- Moriya N, et al Intestinal absorption of serrapeptase (TSP) in rats . Biotechnol Appl Biochem. (1994)
- Woodley JF Enzymatic barriers for GI peptide and protein delivery . Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. (1994)
- KV S, Devi GS, Mathew ST Liposomal formulations of serratiopeptidase: in vitro studies using PAMPA and Caco-2 models . Mol Pharm. (2008)
- Camenisch G, Folkers G, van de Waterbeemd H Shapes of membrane permeability-lipophilicity curves: extension of theoretical models with an aqueous pore pathway . Eur J Pharm Sci. (1998)
- Obata K, et al Prediction of oral drug absorption in humans by theoretical passive absorption model . Int J Pharm. (2005)
- Nirale NM, Menon MD Topical formulations of serratiopeptidase: development and pharmacodynamic evaluation . Indian J Pharm Sci. (2010)
- Shah MH, Paradkar A Cubic liquid crystalline glyceryl monooleate matrices for oral delivery of enzyme . Int J Pharm. (2005)
- Kakinuma A, et al Repression of fibrinolysis in scalded rats by administration of Serratia protease . Biochem Pharmacol. (1982)
- Al-Khateeb TH, Nusair Y Effect of the proteolytic enzyme serrapeptase on swelling, pain and trismus after surgical extraction of mandibular third molars . Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. (2008)
- Kee WH, et al The treatment of breast engorgement with Serrapeptase (Danzen): a randomised double-blind controlled trial . Singapore Med J. (1989)
- Malshe PC A preliminary trial of serratiopeptidase in patients with carpal tunnel Syndrome . J Assoc Physicians India. (2000)
- Jadav SP, et al Comparison of anti-inflammatory activity of serratiopeptidase and diclofenac in albino rats . J Pharmacol Pharmacother. (2010)
- Tachibana M, et al A multi-centre, double-blind study of serrapeptase versus placebo in post-antrotomy buccal swelling . Pharmatherapeutica. (1984)
- Chopra D, et al A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study comparing the efficacy and safety of paracetamol, serratiopeptidase, ibuprofen and betamethasone using the dental impaction pain model . Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. (2009)
- Murugesan K, Sreekumar K, Sabapathy B Comparison of the roles of serratiopeptidase and dexamethasone in the control of inflammation and trismus following impacted third molar surgery . Indian J Dent Res. (2012)
- Panagariya A, Sharma AK A preliminary trial of serratiopeptidase in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome . J Assoc Physicians India. (1999)
- Esch PM, Gerngross H, Fabian A Reduction of postoperative swelling. Objective measurement of swelling of the upper ankle joint in treatment with serrapeptase– a prospective study . Fortschr Med. (1989)
- Bracale G, Selvetella L Clinical study of the efficacy of and tolerance to seaprose S in inflammatory venous disease. Controlled study versus serratio-peptidase . Minerva Cardioangiol. (1996)
- Relevant Role of Fibronectin-Binding Proteins in Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm-Associated Foreign-Body Infections
- Christner M, et al The giant extracellular matrix-binding protein of Staphylococcus epidermidis mediates biofilm accumulation and attachment to fibronectin . Mol Microbiol. (2010)
- Kaplan JB Biofilm dispersal: mechanisms, clinical implications, and potential therapeutic uses . J Dent Res. (2010)
- Artini M, et al Comparison of the action of different proteases on virulence properties related to the staphylococcal surface . J Appl Microbiol. (2013)
- Artini M, et al A new anti-infective strategy to reduce adhesion-mediated virulence in Staphylococcus aureus affecting surface proteins . Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. (2011)
- Longhi C, et al Protease treatment affects both invasion ability and biofilm formation in Listeria monocytogenes . Microb Pathog. (2008)
- Influence of interfaces on microbial activity
- Costerton JW, et al Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease . Annu Rev Microbiol. (1987)
- Lee HS, et al A technique for quantitative cytology of nasal secretions . Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. (1991)
- Nakamura S, et al Effect of the proteolytic enzyme serrapeptase in patients with chronic airway disease . Respirology. (2003)
- Majima Y, et al Effects of orally administered drugs on dynamic viscoelasticity of human nasal mucus . Am Rev Respir Dis. (1990)
- Majima Y, et al The effect of an orally administered proteolytic enzyme on the elasticity and viscosity of nasal mucus . Arch Otorhinolaryngol. (1988)
- Shimura S, et al Effect of expectorants on relaxation behavior of sputum viscoelasticity in vivo . Biorheology. (1983)
- Mecikoglu M, et al The effect of proteolytic enzyme serratiopeptidase in the treatment of experimental implant-related infection . J Bone Joint Surg Am. (2006)
- Ishihara Y, Kitamura S, Takaku F Experimental studies on distribution of cefotiam, a new beta-lactam antibiotic, in the lung and trachea of rabbits. II. Combined effects with serratiopeptidase . Jpn J Antibiot. (1983)
- Aratani H, Tateishi H, Negita S Studies on the distributions of antibiotics in the oral tissues: Experimental staphylococcal infection in rats, and effect of serratiopeptidase on the distributions of antibiotics (author’s transl) . Jpn J Antibiot. (1980)
- Viswanatha Swamy AH, Patil PA Effect of some clinically used proteolytic enzymes on inflammation in rats . Indian J Pharm Sci. (2008)
- Shimizu H, et al A case of serratiopeptidase-induced subepidermal bullous dermatosis . Br J Dermatol. (1999)
- Mazzone A, et al Evaluation of Serratia peptidase in acute or chronic inflammation of otorhinolaryngology pathology: a multicentre, double-blind, randomized trial versus placebo . J Int Med Res. (1990)